MARKETING AND SALES MANAGEMENT
CHECK POINT 94: SALES PLANNING AND BUDGETING
Please Select Any Topic In Check Point 94 Below And Click. |
| |
| |
|
DO I NEED TO KNOW THIS CHECK POINT?
|
|
1. THE SALES PLANNING AND BUDGETING PROCESS |
 |
|
THE SALES PLANNING AND BUDGETING PROCESS |
Business owners and sales managers must remember that sales planning and budgeting is one of the key sales management functions in every business organization.
The first important function of the sales manager is to initiate the Sales Planning And Budgeting Process. This process should be implemented by the sales manager in accordance with realistic estimates of the sales volume likely to be achieved during the forthcoming fiscal period.
The sales planning and budgeting process normally entails three steps outlined below. |
STEPS IN THE SALES PLANNING AND BUDGETING PROCESS

Step 1: Appropriate Market Analysis.
Identify market segments where your company is planning to do business.

Step 2: Measurement Of Sales Potential.
Estimate the sales potential of each market segment in accordance with marketing intelligence information at your disposal.

Step 3: Sales Forecasting.
Develop sales forecasts based on realistic expectations in accordance with the existing conditions in the marketplace and your company's internal abilities. |
|
|
|
2. SALES POTENTIAL |
 |
|
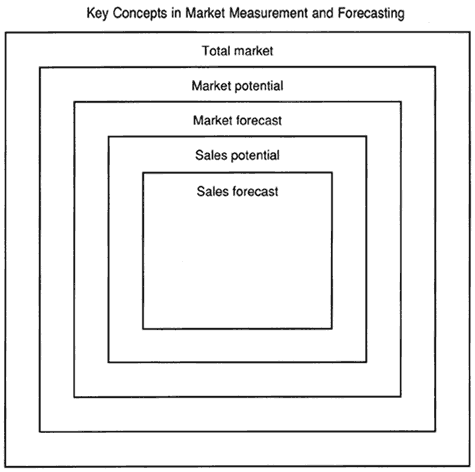
SALES POTENTIAL IS A PART OF MARKET MEASUREMENT AND FORECSATING
The process of estimating Sales Potential for various products and services has been described in detail in this Tutorial. This process represents a part of the market measurement and forecasting procedure, and it is illustrated below. |
KEY CONCEPTS IN MARKET MEASUREMENT AND FORECASTING |
| |
 |
| |
SALES POTENTIAL
There are several methods for determining sales potential for products or services in the specific market. Some of these methods for assessing the Current Market Demand and Sales Potential are explained in detail in Tutorial 5.
Evaluation of the company's sales potential in selected market segments helps management in preparing more accurate sales forecasts. Three of these methods are mentioned below. |
THREE METHODS FOR DETERMINING SALES POTENTIAL
 |
|
 |
|
 |
The
Chain-Ratio
Method |
|
The
Market-Buildup
Method |
|
The
Buying-Power-Index
Method |
| |
|
|
|
3. SALES FORECAST |
 |
|
SALES FORECASTS
Sales Forecasts provides a quantitative estimate of the level of actual sales, expressed in monetary terms, or of units of product to be sold during a specified period of time. The sales forecast is usually prepared on an annual basis, taking into consideration several factors illustrated below. |
SALES FORECASTING FACTORS
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Past
Sales
Performance |
|
Existing
Market
Conditions |
|
Product
Demand
Fluctuations |
|
Competition |
|
|
| |
IMPORTANCE OF SALES FORECASTS
Sales Forecast provides an important foundation for the financial, production, and human resources departments to plan their work and ascertain their needs for the forthcoming budgeted period. Managers, however, must be careful in using the sales forecast estimates for two reasons outlined below. |
WHY SHOULD MANAGERS BE CAREFUL WITH SALES FORECASTS? |
No. |
Details |
1. |
If the sales forecast is too optimistic, the company can sustain substantial losses as a result of an over-expenditure of funds in anticipation of an income level that has not been achieved. |
2. |
If the sales forecast is too low, the company may not be in a position to accommodate all market needs and may subsequently forgo profits and present its competitors with additional sales opportunities. |
|
There are several Sales Forecasting Methods commonly used by managers in preparing sales forecasts. Three of these methods are illustrated below. |
SALES FORECASTING METHODS
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Sales Force
Composite
Opinion |
|
Jury Of
Executive
Opinion |
|
Survey Of
Buying
Intentions |
|
|
|
|
4. SALES FORCE COMPOSITE OPINION |
 |
|
SALES FORCE COMPOSITE OPINION
Sales Force Composite Opinion is a popular sales forecasting method frequently used by sales managers.
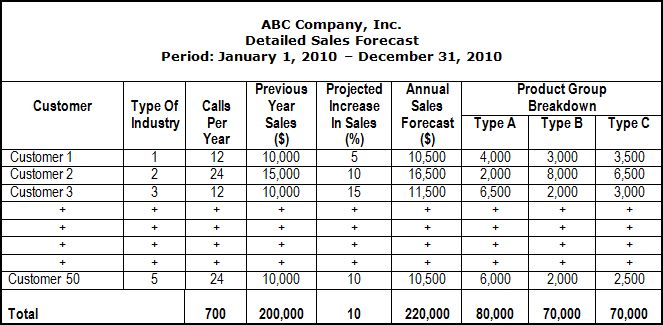
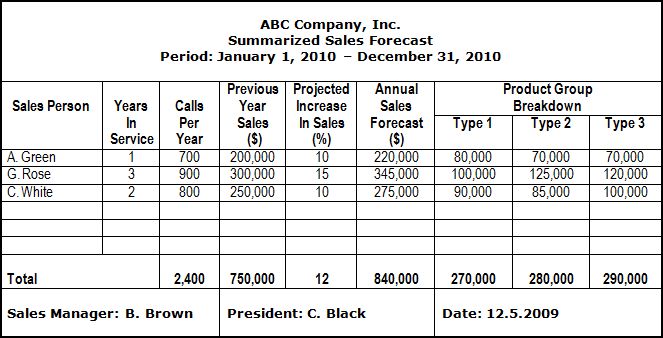
In accordance with this method, each sales person is required to prepare Individual Sales Projections for the forthcoming fiscal year and to submit a detailed sales forecast to the sales manager. These projections, illustrated in the Detailed Sales Forecast below, must be based on realistic sales estimates, taking into consideration past results and future expectations. Subsequently, all sales projections must be added up in a Summarized Sales Forecast to obtain the final forecast of sales volume as illustrated below.
Active participation by each member of the sales team and preparation of the sales forecast by customer, product, and sales territory represent the major advantages of this method. |
|
|
|
5. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
DETAILED SALES FORECAST |
 |
|
DETAILED SALES FORECAST |
 |
|
6. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
SUMMARIZED SALES FORECAST |
 |
|
SUMMARIZED SALES FORECAST |
 |
|
7. JURY OF EXECUTIVE OPINION |
 |
|
JURY OF EXECUTIVE OPINION
Jury Of Executive Opinion is another forecasting method commonly used by sales managers. This method is based on Sales Forecasts prepared by several members of the company's management team. All participating executives prepare an individual sales forecast using their own judgment. Subsequently, all individual sales projections are evaluated and finally added up.
Active participation by the company's executives has proven to be useful in preparing accurate short-term forecasts. This method, however, demands substantial experience and understanding of overall requirements in the marketplace. Several factors that are usually considered during the Jury Of Executive Opinion procedure are outlined below. |
JURY OF EXECUTIVE OPINION FACTORS
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Nature Of
Company's
Products
Or Services |
|
Customers'
Requirements |
|
Competition |
|
Economic
Conditions In
The Marketplace |
| |
|
|
|
8. SURVEY OF BUYING INTENTIONS |
 |
|
SURVEY OF BUYING INTENTIONS
A Survey Of Buying Intentions can be used as an alternative or an addition to the above mentioned sales forecasting methods. This method entails surveying a sample of customers to determine the types and quantities of products or services they are likely to buy in the future.
A survey of buying intentions may be conducted by using a broad range of communication media illustrated below. |
COMMUNICATION MEDIA USED IN A SURVEY OF BUYING INTENTIONS
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Personal
Interviews |
|
Phone |
|
Mail
Questionnaires |
|
Internet |
|
|
| |
IMPORTANCE OF USING SEVERAL SALES FORECASTING METHODS
In a Survey Of Buying Intentions, all customer responses are subsequently evaluated and added up to determine the total demand for each product.
This method has proven to be useful in preparing sales forecasts for industrial goods in well-defined small market segments. However, it is often a time consuming and expensive method that does not guarantee that interviewed customers will always act according to their original answers and intentions.
Since most organizations offer a variety of products or services to different customers in a constantly changing market environment, it is often impractical to use only one sales forecasting method. For this reason, sales managers often use a combination of methods and utilize the input from sales people, executive managers, and customers at the same time. |
|
|
9. SALES STRATEGIES |
 |
|
SALES STRATEGIES
Once Sales Forecasts are prepared and overall Sales Objectives are established, it is necessary to develop a detailed Sales Plan which will provide guidance to the company's management in the process of achieving their objectives.
A well-defined plan must be based on a set of appropriate Sales Strategies for the forthcoming fiscal year. These strategies represent the continuation of the Marketing Strategies which are discussed in detail in Tutorial 5. Some examples of sales strategies that could be adopted by a sales manager are outlined below. |
DEVELOPMENT OF SALES STRATEGIES |

Marketing Strategies

|

|

|

|

|
New Venture
Strategy |
Growth
Strategy |
Market
Development
Strategy |
Market
Retention
Strategy |
Balancing
Strategy |

|

|

|

|

|
Develop A Set Of Appropriate Sales Strategies

|

|

|

|

|
Sell New
Products Or
Services To
Existing
Customers |
Offer More
Attractive Discounts To Existing Customers |
Offer
Improved
Products Or
Services At
Reduced
Prices |
Reduce
Product Or
Service Range
And Increase
The Sales
Volume |
Sell Existing
Products Or
Services And
Maintain The
Sales Volume |

|

|

|

|

|
Reduce Price Of Existing Products Or Services And Offer These To Current And Potential Customers |
Offer Excess Inventory To Customers At Reduced Prices |

|

|

|

|

|
Demonstrate
The Advantages
Of New Products
Or Services |
Introduce
New Sales
Promotion
Methods |
Develop
New Accounts
And Eliminate
Unprofitable
Accounts |
Reduce
Marketing
And Sales
Overheads |
Eliminate
Unprofitable
Product Or
Service Lines |
|
|
|
10. EVALUATION OF THE SALES FORCE REQUIREMENTS |
 |
|
THE SALES FORCE REQUIREMENTS
The next step in the sales planning effort entails Evaluation Of Sales Force Requirements to meet the company’s sales objectives. The sales manager must assess the overall sales plan, evaluate each of the three options presented below, and select the most appropriate option. |
THREE OPTIONS IN THE SALES FORCE REQUIREMENTS
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Reduce
The Sales Force |
|
Maintain
The Sales Force |
|
Increase
The Sales Force |
| Reduce the present number of sales people. |
|
Maintain the present number of sales people. |
|
Increase the present number of sales people. |
| |
|
If the number of sales people must be increased, the sales manager must make a choice between two options outlined below. |
TWO OPTIONS FOR INCREASING THE SALES FORCE
No. |
Details |
1. |
To use outside agents. |
2. |
To hire new sales people. |
|
|
|
11. ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF USING OUTSIDE AGENTS |
 |
|
SALES AGENTS OR INDEPENDENT REPRESENTATIVES
One of the options available to business owners and sales managers is to employ outside Sales Agents or Independent Sales Representatives (Sales Reps) to sell the company’s products and services in the marketplace. The use of agents or independent representatives has several advantages outlined below. |
ADVANTAGES OF USING OUTSIDE AGENTS |
No. |
Details |
1. |
Sales agents already have a network of well-established contacts. |
2. |
Sales agents usually have good experience in their product lines and maintain high standards of work. |
3. |
Sales agents do not incur administrative costs for a company. |
4. |
Sales agents get paid only if they are successful in selling the company’s products or services. |
|
| |
DISADVANTAGES OF USING OUTSIDE SALES AGENTS
One of the prime disadvantages in dealing with sales agents is that their activities cannot always be effectively controlled by the sales manager. This may present a particular problem since sales agents plan their own movements in the marketplace and work according to their own time schedules. |
|
|
12. ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF USING SALES PEOPLE |
 |
|
SALES PEOPLE
Another option that can be exercised by the business owner and the sales manager is to hire Sales People. This option may also present certain advantages and disadvantages which are summarized below. |
ADVANTAGES OF USING SALES PEOPLE |
No. |
Details |
1. |
Sales people can be trained according to the company's specific requirements. |
2. |
Sales people can be allocated to defined sales territories, customers, and product or service lines. |
3. |
The performance of sales people can be planned as a part of the overall sales effort. |
4. |
The performance of sales people can be monitored and controlled on a regular basis. |
|
| |
COST OF USING SALES PEOPLE
The employment of sales people may represent a costly exercise. It is essential, therefore, to assess the need for additional sales employees and to estimate the total cost of their employment. Estimating the Sales Force size entails a number of considerations and may be carried out in several ways.
Two Methods For Estimating The Sales Force Requirements commonly used by business owners and sales managers are illustrated below. |
METHODS FOR ESTIMATING THE SALES FORCE REQUIREMENTS
 |
|
 |
The "How Much Can
The Company Afford" Method |
|
The "Number
Of Sales Calls" Method |
| |
|
|
|
13. THE "HOW MUCH CAN THE COMPANY AFFORD" METHOD |
 |
|
THE "HOW MUCH CAN THE COMPANY AFFORD" METHOD
The "How Much Can The Company Afford" Method is based on matching two basic variables outlined below. This method has an advantage since all sales costs will remain in line with the company's projected revenues. The main disadvantage, however, is that this method does not account for the real needs of customers in the marketplace. |
TWO VARIABLES OF THE
"HOW MUCH CAN THE COMPANY AFFORD" METHOD |
No. |
Details |
1. |
A number of sales people at a pre-determined average cost per employee. |
2. |
A specific sales budget allocation. |
|
|
|
14. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
THE "HOW MUCH CAN A COMPANY AFFORD" METHOD |
 |
|
THE "HOW MUCH CAN A COMPANY AFFORD" METHOD
Consider, for example, a medium-sized company that:
| • |
Projects $10 million in sales for the forthcoming fiscal year. |
| • |
Allocates 5 percent of its revenue toward sales activities. |
Assume that:
| • |
Sales supervision requires 20 percent of the sales budget. |
| • |
The total cost of each sales person is $50,000 per year, including straight salary, commission, and travel allowance. |
Description |
Calculation |
Result |
Total Budgeted Revenue From Sales |
- |
$10,000,000 |
Total Sales Budget Allocation |
$100,000 x 0.05 |
$500,000 |
Total Cost Of Sales Supervision |
$500,00 x 0.2 |
$100,00 |
Total Cost Allocated
To The Sales Force |
$500,000 - $100,000 |
$ 400,000 |
Total Number Of Sales People |
At $50,000 Per Sales Person Per Year |
8 Sales People |
|
|
|
15. THE "NUMBER OF SALES CALLS" METHOD |
 |
|
THE "NUMBER OF CALLS" METHOD
The "Number Of Sales Calls" Method, on the other hand, is designed to develop a sales force in accordance with specific customer needs. This method takes into account four variables outlined below. (47)
The size of the sales force can be determined as follows:
| Number Of Sales People = |
(A + B ) x C x D |
| E |
|
FOUR VARIABLES IN THE "NUMBER OF CALLS" METHOD |
No. |
Details |
1. |
The number of existing and potential customers. |
2. |
The average number of sales calls per year required by each customer. |
3. |
The length of each sales call. |
4. |
The selling time available per sales person. |
|
| |
FORMULA KEY: |
No. |
Details |
A |
Number of existing customers. |
B |
Number of potential customers. |
C |
Required sales call frequency. |
D |
Average length of a sales call. |
E |
Selling time available per sales person. |
|
| |
ADVANTAGES OF THE "NUMBER OF CALLS" METHOD
The "Number Of Sales Calls" Method enables the sales manager to determine the required size of the company's sales force well in advance in accordance with specific customer needs.
One of the drawbacks of this method, however, is its failure to account for income and expenditures associated with different aspects of customer service. Thus, it becomes difficult to establish whether the current frequency of sales calls enables the company to maximize its profits through servicing customers. |
|
|
16. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
THE "NUMBER OF SALES CALLS" METHOD |
 |
|
THE "NUMBER OF SALES CALLS" METHOD
Consider, for example, a medium-sized company that:
| • |
Has 200 existing customers. |
| • |
Plans to open 50 additional new accounts. |
Assume that:
| • |
Each customer should ideally be called at least once every two months, or six times a year. |
| • |
Each sales call requires an average of two hours, including travel time. |
| • |
The selling time available per sales person is 1,500 hours per year. |
The size of the sales force can be determined as follows:
| Number Of Sales People = |
(200 + 50) x 6 x 2 |
= 2 Sales People |
| 1,500 |
In reality, however, the company's customers usually vary in size and subsequently will have different needs. These needs, in turn, should be translated into:
An ideal frequency of sales calls per year for each customer.
Consider, for example, that the company has:
| • |
40 large present and potential customers that require 18 calls per year. |
| • |
100 medium-sized customers that require 12 calls per year. |
| • |
110 small customers that require 3 calls per year. |
Assuming that the average length of each sales call and the selling time per sales person remain unchanged, the size of the sales force can be determined as follows:
| Number Of Sales People = |
[(40 x 18) + (100 x 12) + (110 x 3)] x2 |
= 3 Sales People |
| 1,500 |
|
|
|
17. ADVANTAGES OF HIRING EXPERIENCED SALES PEOPLE |
 |
|
HIRING OF SALES PEOPLE
Once the size of the sales force is determined, it becomes necessary to decide between hiring experienced or inexperienced Sales People, as illustrated below. Thus, the final decision regarding the choice of suitable sales people remains with the business owner or the sales manager. |
TWO OPTIONS FOR HIRING SALES PEOPLE
 |
|
 |
Hiring Experienced
Sales People |
|
Hiring Inexperienced
Sales People |
| Hiring experienced sales people will enable the company to respond to immediate market demands and to provide better service to customers. However, the high compensation package often required by experienced sales people may be a deterrent. |
|
Hiring inexperienced sales people may be less costly in terms of the compensation package, but it will require additional investment in sales training. In the long run this may not be the most cost-effective option. |
|
|
|
|
18. SALES BUDGET |
 |
|
SALES BUDGET
The ultimate task of the sales planning process is development of a sound Sales Budget. All components of the sales budget must be prepared on an annual basis and thereafter divided into monthly targets in accordance with relevant sales projections.
The sales budget summarizes all details related to several important elements outlined below. |
ELEMENTS OF A SALES BUDGET |
No. |
Details |
1. |
The projected level of the company’s sales throughout the budgeted period. |
2. |
The selling expenditure budget, including salaries and commissions of sales employees. |
3. |
The advertising budget. |
4. |
The sales administration budget. |
|
|
|
19. THE SALES BUDGETING PROCESS |
 |
|
THE SALES BUDGETING PROCESS
The main purpose of the Sales Budgeting Process is to enable the management team to lead its organization toward a predetermined goal and to achieve the desired level of the company's profitability. A typical sales budgeting process entails a number of steps outlined below. |
STEPS IN THE SALES BUDGETING PROCESS

Step 1: Become Familiar With The Company's Marketing Plan.

Step 2: Formulate The Company's Sales Objectives In Accordance With The Company's Marketing Plan.

Step 3: Prepare Annual Sales Forecasts Per Product, Or Service, Or Customer, Or Sales Territory, Or A Combination Thereof.

Step 4: Identify Personal Selling And Promotional Requirements Needed To Meet The Company's Sales Objectives.

Step 5: Summarize Estimated Values Of Annual Sales Forecasts And Selling Costs And Prepare A Budget.

Step 6: Compare Actual Sales Revenues And Selling Costs With The Budgeted Values On A Monthly Basis And Identify Budget Variances.

Step 7: Evaluate All Budget Variances And Use Them For Controlling Purposes And For Further Budget Revisions (Refer back to Step 5). |
|
|
20. SALES BUDGETING FACTORS |
 |
|
SALES BUDGETING
The Sales Budget must be prepared by the sales manager in accordance with realistic estimates of sales volume likely to be achieved during the forthcoming fiscal period.
Main factors that usually influence the Sales Budgeting Process, discussed in Tutorial 3, are outlined below. As a result of detailed evaluation of these factors, the sales manager is expected to prepare accurate sales budgets pertaining to all products or services offered by the company. |
SALES BUDGETING FACTORS |
No. |
Details |
1. |
Nature of the company's products and services. |
2. |
History of previous sales. |
3. |
Seasonal variations in product or service demand. |
4. |
The company's current position in the marketplace. |
5. |
Influence by competitors. |
6. |
The company's plans for new product or service development. |
7. |
Expected product or service demand in the marketplace. |
8. |
Economic stability in the marketplace. |
9. |
Rate of inflation. |
|
Sales budgets provide quantitative estimates of the level of sales, expressed in various terms, as illustrated below. |
TERMS OR UNITS USED IN THE SALES BUDGET
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Monetary
Terms |
|
Units Of Product
To Be Sold |
|
Units Of Service
To Be Rendered |
| |
|
A simplified Sales Budget for a company is presented below. |
|
|
21. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
SALES BUDGET |
 |
|
SALES BUDGET
ABC Corporation
Sales Budget
Period: January 1, 2013 - December 31, 2013 |
Product Or Service
Description |
Estimated Value ($) |
Annual |
Monthly |
Product (Service) Type A |
900,000 |
75,000 |
Product (Service) Type B |
600,000 |
50,000 |
Product (Service) Type C |
300,000 |
25,000 |
Product (Service) Type D |
300,000 |
25,000 |
Total Projected Sales (Revenue) |
2,100,000 |
175,000 |
Sales Manager:
B. Blue |
President:
C. Gray |
Date:
December 20, 2012 |
|
|
|
|
22. FOR SERIOUS BUSINESS OWNERS ONLY |
 |
|
ARE YOU SERIOUS ABOUT YOUR BUSINESS TODAY? |

Reprinted with permission. |
|
23. THE LATEST INFORMATION ONLINE |
 |
|
|
| |
LESSON FOR TODAY:
If You Don't Know Where You Are Going -
You Might Wind Up Someplace Else!
Yogi Berra |
| |
|







