MARKETING AND SALES MANAGEMENT
CHECK POINT 99: SALES FORCE MANAGEMENT AND MOTIVATION
This Check Point Is Available By Subscription Only,
But You Can Still Check Out The Menu Below. |
|
| |
|
DO I NEED TO KNOW THIS CHECK POINT?
|
| |
MARKETING AND SALES MANAGEMENT
CHECK POINT 99: SALES FORCE MANAGEMENT AND MOTIVATION
Please Select Any Topic In Check Point 99 Below And Click.
|
|
| |
|
DO I NEED TO KNOW THIS CHECK POINT?
|
| |
WELCOME TO CHECK POINT 99 |
|
| |
HOW CAN YOU BENEFIT FROM CHECK POINT 99? |
| |
| The main purpose of this check point is to provide you and your management team with detailed information about Sales Force Management And Motivation and how to apply this information to maximize your company's performance. |
| |
| In this check point you will learn: |
| |
• About tasks and steps in the sales force management and motivation process.
• About reasons for establishing sales territories.
• About evaluating the sales territory planning factors.
• About selecting and designing four basic types of sales territories.
• About a geographically-based sales territory.
• About a product-based sales territory.
• About a customer-based sales territory.
• About a combined sales territory.
• About steps in designing a sales territory.
• About assigning sales people to selected sales territories... and much more. |
| |
LEAN MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES FOR CHECK POINT 99 |
| |
| You and your management team should become familiar with the basic Lean Management principles, guidelines, and tools provided in this program and apply them appropriately to the content of this check point. |
| |
| You and your team should adhere to basic lean management guidelines on a continuous basis: |
| |
| • |
Treat your customers as the most important part of your business. |
| • |
Provide your customers with the best possible value of products and services. |
| • |
Meet your customers' requirements with a positive energy on a timely basis. |
| • |
Provide your customers with consistent and reliable after-sales service. |
| • |
Treat your customers, employees, suppliers, and business associates with genuine respect. |
| • |
Identify your company's operational weaknesses, non-value-added activities, and waste. |
| • |
Implement the process of continuous improvements on organization-wide basis. |
| • |
Eliminate or minimize your company's non-value-added activities and waste. |
| • |
Streamline your company's operational processes and maximize overall flow efficiency. |
| • |
Reduce your company's operational costs in all areas of business activities. |
| • |
Maximize the quality at the source of all operational processes and activities. |
| • |
Ensure regular evaluation of your employees' performance and required level of knowledge.
|
| • |
Implement fair compensation of your employees based on their overall performance.
|
| • |
Motivate your partners and employees to adhere to high ethical standards of behavior. |
| • |
Maximize safety for your customers, employees, suppliers, and business associates. |
| • |
Provide opportunities for a continuous professional growth of partners and employees. |
| • |
Pay attention to "how" positive results are achieved and constantly try to improve them. |
| • |
Cultivate long-term relationships with your customers, suppliers, employees, and business associates. |
|
|
|
1. STEPS IN THE SALES FORCE MANAGEMENT AND MOTIVATION PROCESS |
 |
|
SALES FORCE MANAGEMENT AND MOTIVATION |
Business owners and sales managers must be fully familiar with effective sales force management and motivation procedures to ensure above-average performance of the organization’s sales team in meeting and exceeding marketing and sales objectives.
The Sales Force Management And Motivation entails a number of activities outlined below. |
SALES FORCE MANAGEMENT AND MOTIVATION PROCESS TASKS |
1. |
Evaluating, selecting, and designing sales territories, if applicable. |
2. |
Assigning sales people to sales territories. |
3. |
Allocating sales quotas to sales people. |
4. |
Implementing a territorial coverage plan. |
5. |
Motivating sales people. |
6. |
Training sales people. |
7. |
Monitoring the performance of the sales people. |
8. |
Conducting regular sales meetings. |
|
A typical Sales Force Management And Motivation Process comprises a number of steps that are summarized below. |
THE SALES FORCE MANAGEMENT AND MOTIVATION PROCESS |
|

Step 1: Evaluate Sales Territory Planning Factors. |

|

|

|

|

|
Type Of
Account |
Marketing
Objectives |
Workload
Allocation |
Time
Allocation |
Sales
Strategies |
| • |
Customer identification. |
| • |
Customer
needs
analysis. |
| • |
Customer classification. |
| • |
Expected value. |
|
| • |
Market share. |
| • |
New business. |
| • |
Company
image. |
| • |
Account
objectives. |
| • |
Product
or service
objectives. |
|
| • |
Number of
accounts. |
| • |
Number
of sales
calls. |
| • |
Duration
of a sales
call. |
| • |
Non-selling
time. |
|
| • |
Value
of time. |
| • |
Return
on time invested. |
| • |
Opportunity
costs. |
|
| • |
Product mix. |
| • |
Territorial
coverage. |
| • |
Sales call frequency patterns. |
| • |
Selling
preferences. |
|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Step 2: Select And Design Sales Territories. |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Geographically-
Based
Sales Territory |
|
Product Or
Service-Based
Sales Territory |
|
Customer-
Based
Sales Territory |
|
Combined
Sales Territory |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
Step 3: Assign Sales People To Selected Sales Territories.

Step 4: Allocate Sales Quotas To Individual Sales People.

Step 5: Implement Sales Territory Coverage Plan. |

|

|

|

|

|
Maintain
Time
Management |
Maintain
Customers'
Records |
Develop
Sales-Call
Schedules |
Prepare
Routing
And Traveling
Plans |
Monitor
Planned
Sales Calls |

|

|

|

|

|
|
Step 6: Motivate Sales People In Meeting Their Objectives.

Step 7: Conduct Regular Sales Meetings. |
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
Please watch these excellent videos professionally narrated and produced by Victor Antonio: |
|
© 2013 Victor Antonio. All rights reserved. |
|
|
2. A SALES TERRITORY |
 |
|
WHAT IS A SALES TERRITORY?
The phrase "sales territory" is misleading because it does not relate to a specific geographic area alone. A sales territory represents a quantifiable and identifiable group of existing and potential buyers. A Sales Territory thus focuses upon sales potential from the company's point of view and would be a slice of the total pie that the company hopes to obtain in sales.
Many companies offer products and services to customers in the marketplace without any restriction to a geographic location. For example, companies may offer products and services to customers online all over the world and in this case the entire world will become the sales territory.
There are several reasons for establishing sales territories as outlined below. (61) |
REASONS FOR ESTABLISHING SALES TERRITORIES |
1. |
Ensuring thorough coverage of the existing and potential market. |
2. |
Increasing motivation and efficiency of sales employees. |
3. |
Optimizing the level of selling costs. |
4. |
Providing better control and evaluation of the sales force. |
5. |
Facilitating improved customer relations. |
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
3. EVALUATE THE SALES TERRITORY PLANNING FACTORS |
 |
|
STEEP 1: EVALUATE THE SALES TERRITORY PLANNING FACTORS
Prior to selecting and designing suitable sales territories, the sales manager must evaluate several Sales Territory Planning Factors. Some of the sales territory's planning factors are outlined below. (62) |
THE SALES TERRITORY PLANNING FACTORS |
1. |
Type Of Account.
This entails identifying existing and potential customers, evaluating their needs, classifying customers into various categories, and estimating their business potential. |
2. |
Marketing Objectives.
This entails examining marketing plan requirements pertinent to market share, new business, company image, account, and product or service objectives. |
3. |
Workload Allocation.
This entails considering the number of accounts handled by a sales person, the required frequency of calls, the average duration of each call, travel time, and non-selling time. |
4. |
Time Allocation.
This entails establishing the value of time for each sales person, determining the required return on time invested, and summarizing opportunity costs such as the overall costs of the selling effort. |
5. |
Sales Strategies.
This entails examining relevant sales strategies regarding product mix, territorial coverage requirements, call frequency patterns, and selling preferences. |
|
Several examples of Sales Strategies are presented in Tutorial 5. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
4. SELECT AND DESIGN SALES TERRITORIES |
 |
|
STEP 2: SELECT AND DESIGN SALES TERRITORIES
Upon completing the evaluation of the aforementioned factors, the sales manager should begin the Selection And Design Of Sales Territories. There are four basic types of sales territories that could be selected by the sales manager as illustrated below. |
FOUR BASIC TYPES OF SALES TERRITORIES |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Geographically-
Based
Sales Territory |
|
Product-
Based
Sales Territory |
|
Customer-
Based
Sales Territory |
|
Combined
Sales Territory |
|
|
| |
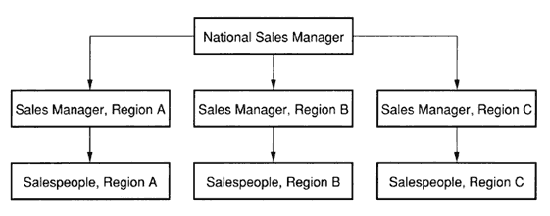
A GEOGRAPHICALLY-BASED SALES TERRITORY |
A Geographically-Based Sales Territory provides a method of assigning the sales force to specified sales territories or regions in which each sales person handles a full range of company products or services. This method enables the sales manager to build a Geographically-Based Sales Organization, as was discussed earlier, and illustrated below. |
|
|
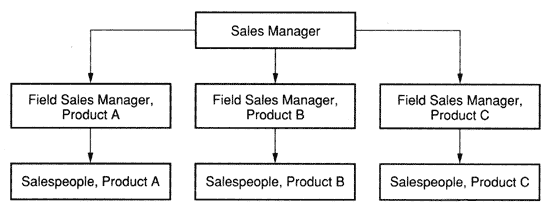
A PRODUCT-BASED SALES TERRITORY |
A Product-Based Sales Territory provides a method whereby sales people are allocated in accordance with a specific product or service range and cover the marketplace without geographic limitation. This method enables the sales manager to build a Product-Specialized Sales Organization, as described earlier, and illustrated below. |
|
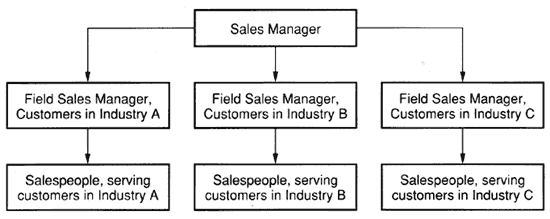
A CUSTOMER-BASED SALES TERRITORY |
A Customer-Based Sales Territory provides a method whereby sales people are assigned to individual customers or to a particular type of industry, and cover the marketplace without geographic limitation. This method enables the sales manager to develop a Customer-Specialized Sales Organization, as discussed earlier, and illustrated below. |
|
COMBINED SALES TERRITORY |
Combined Sales Territory represents a method which enables the sales manager to utilize all three aforementioned methods on a selective basis. The Combined Sales Territory Method of sales force allocation enables the company to remain flexible and satisfy market demands at any given time. This method is outlined below. |
THE COMBINED SALES TERRITORY METHOD |
1. |
The first group of sales people may be required to operate in a limited geographic area and allocated to geographically-based sales territories. |
2. |
The second group of sales people may be required to handle a limited number of products in the marketplace and allocated to product-based sales territories. |
3. |
The last group may be assigned to individual customers or industries and allocated to customer-based sales territories. |
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
5. STEPS IN DESIGNING A SALES TERRITORY |
 |
|
DESIGN THE SALES TERRITORY
If the sales manager selects the first type, Geographically-Based Sales Territory, the territory needs to be designed further.
According to Douglas J. Dalrymple, the Sales Territory Design Process consists of five steps outlined below. (63) |
THE SALES TERRITORY DESIGN PROCESS |

Step 1: Select A Geographic Control Unit.

Step 2: Decide On Allocation Factors.

Step 3: Select The Starting Points.

Step 4: Combine Adjacent Control Units.

Step 5: Compare Sales Territories Based On Allocation Factors. |
| |
GEOGRAPHIC CONTROL UNITS |
First, the sales manager must select suitable Geographic Control Units in order to form and develop Sales Territories. This process is illustrated below. |
TYPES OF THE GEOGRAPHIC CONTROL UNITS |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
| ZIP Code Area |
|
City |
|
County |
|
State |
|
|
| |
SELECT A SUITABLE GEOGRAPHIC CONTROL UNIT |
The first three types of "Geographic Control Units" are used more frequently since their size provides sufficient flexibility in setting boundaries for sales territories.
States are generally too large for sales territory design purposes. However, State-Based Geographic Control may provide a sound overview for overall planning purposes. The choice of a suitable geographic control unit also depends upon the availability of statistical information on population, number of companies, or volume of sales in each area. |
DECIDE ON ALLOCATION FACTORS |
Second, the sales manager must decide on Allocation Factors for combining different control units into sales territories. This means that sales territories should be designed so that each sales person has a fair opportunity to meet organizational and personal objectives. There are two allocation factors frequently used by sales managers in designing sales territories as outlined below. |
TWO ALLOCATION FACTORS FOR DESIGNING SALES TERRITORIES |
1. |
Current Number Of Customers.
The current number of customers provides a realistic estimate of the existing workload in a particular sales territory. |
2. |
Overall Number Of Customers.
The overall number of customers may provide a good estimate of the total workload potential in a specified sales territory. |
|
| |
SELECT THE STARTING POINTS |
|
Third, the sales manager must choose Starting Points for various sales territories. Probably the most practical approach is to identify the largest concentration of existing or potential customers and to use that as the "starting point" in developing a particular sales territory.
From this point the sales manager may expand the Sales Territory in other directions to cover a larger area. Sometimes the sales person's home may be used as the starting point. In this instance, each sales person is required to develop a sales territory around his or her home as part of an overall selling effort. |
COMBINE ADJACENT CONTROL UNITS |
|
Fourth, the sales manager must combine Adjacent Control Units in order to complete the design of new sales territories. Thus, for example, if the potential number of customers per county is used as the Allocation Factor, it is necessary to determine the total required number of customers and develop sales territories accordingly.
A typical illustration of combining adjacent control units is presented below. |
COMPARE SALES TERRITORIES BASED ON ALLOCATION FACTORS |
Finally, the sales territories design process entails the Comparison Of Individual Sales Territories using different criteria.
For example, a Set Of Sales Territories can be compared on the basis of square mileage or number of customers in each territory. Such a comparison enables the sales manager to ensure a balanced allocation of workload and provide fair opportunity to each sales person in meeting sales objectives.
|
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
6. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
SALES TERRITORY DESIGN |
 |
|
SALES TERRITORY DESIGN |
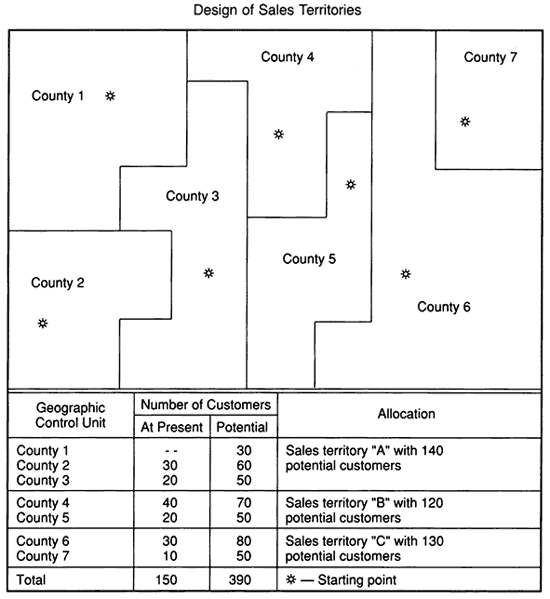
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
7. ASSIGN SALES PEOPLE TO SELECTED SALES TERRITORIES |
 |
|
STEP 3: ASSIGN SALES PEOPLE TO SELECTED SALES TERRITORIES
Once the sales territories are designed, it is necessary to allocate suitable sales people and to proceed with implementation of the overall sales program. This step is required if the company offers products and services in geographically-based sales territory.
The Allocation Of Sales People depends upon a number of factors outlined below. |
SALES EMPLOYEES ALLOCATION FACTORS |
1. |
Number of sales people in the company at present. |
2. |
Past performance of each individual sales person. |
3. |
Company's specific needs in a particular sales territory. |
4. |
Market potential in a particular sales territory. |
5. |
Personal experience and preferences of each sales person. |
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
8. ALLOCATE SALES QUOTAS TO INDIVIDUAL SALES PEOPLE |
 |
|
STEP 4: ALLOCATE SALES QUOTAS TO INDIVIDUAL SALES PEOPLE
Effective utilization of sales people cannot be accomplished without establishing detailed Sales Volume Quotas or Sales Quotas. The type of sales quotas, or Sales Targets, selected by the sales manager depends upon several factors outlined below. |
FACTORS IN ESTABLISHING SALES QUOTAS |
1. |
The nature of the product or service provided by the company. |
2. |
Defined sales territories, if applicable. |
3. |
Type and number of customers. |
4. |
The existing structure of the sales force. |
|
| |
SALES QUOTAS |
A Sales Quota represents a basic sales performance goal that is assigned to a sales person, agent, or customer during a specific period of time.
Sales quotas assist in the process of planning, controlling, and evaluating the overall selling effort of the organization. Some of the major objectives for establishing sales quotas are summarized below. |
OBJECTIVES FOR ESTABLISHING SALES QUOTAS |
1. |
To indicate strengths and weaknesses of the selling structure. |
2. |
To provide quantified objectives and incentives for the sales force. |
3. |
To provide management with a tool for measuring and controlling sales performance. |
4. |
To facilitate effective compensation of the sales employees. |
|
| |
SETTING SALES QUOTAS |
|
Sales Quotas are usually set in conjunction with the estimated territorial potential of the market, or, alternatively, in accordance with the company's Sales Forecasts. Quotas are frequently set on the basis of past sales experience and may also be related to a specific compensation plan designed to motivate the sales force of the organization.
The effectiveness of the Sales Quota System usually depends upon its acceptance by the sales force and cooperation among the sales employees. All sales quotas should be recorded in the Annual Sales Quota Report as illustrated below. |
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
9. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
ANNUAL SALES QUOTA REPORT |
 |
|
ANNUAL SALES QUOTA REPORT |
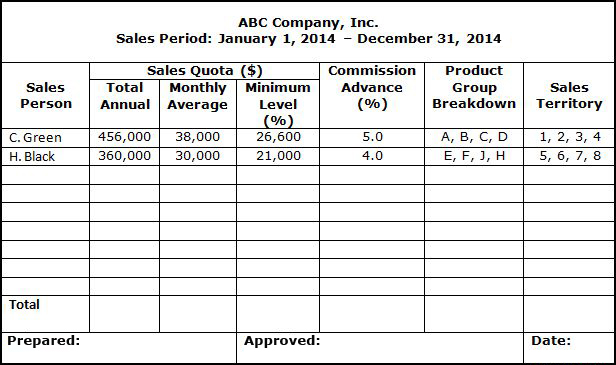 |
|
|
10. IMPLEMENT SALES TERRITORY COVERAGE PLAN |
 |
|
STEP 5: IMPLEMENT SALES TERRITORY COVERAGE PLAN |
Once sales quotas are allocated to individual sales people, the implementation of a sales territory coverage plan can begin. The sales manager should provide Continuous Guidance To Each Sales Person in an effort to produce the desired results. This entails guidance in several areas illustrated below. |
AREAS OF GUIDANCE REQUIRED BY SALES PEOPLE |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Time
Management |
|
Maintenance
Of Customers'
Records |
|
Development
Of Sales-Call
Schedules |
|
Selection
Of
Sales Routes |
|
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
11. TIME MANAGEMENT |
 |
|
IMPORTANCE OF TIME MANAGEMENT
Effective Time Management is a critical element of successful selling performance. It is essential, therefore, that the sales manager guides each sales person in time management. This is particularly important since sales people are involved in a variety of activities outlined below. |
TYPICAL ACTIVITIES OF SALES PEOPLE |
1. |
Calling prospects on the phone and making sales appointments. |
2. |
Traveling to sales appointments. |
3. |
Face-to-face sales appointments. |
4. |
Selling to customers on the phone. |
5. |
Preparing estimates for customers. |
6. |
Completing service calls to customers. |
7. |
Preparing reports for sales meetings. |
8. |
Attending sales meetings. |
9. |
Communicating with prospects and customers online. |
|
| |
MINIMIZE TIME-WASTING HABITS |
In order to ensure that the time allocated to each sales person is spent in the most productive manner, it is necessary to minimize or eliminate various Time-Wasting Habits. Continuous reduction or elimination of these habits helps sales people develop effective sales-call schedules and produce excellent results.
Several common Time-Wasters are summarized below. |
COMMON TIME-WASTING FACTORS |
General Types
Of Time-Wasting Factors |
Time-Wasting Factors
Specific To The Sales Area |
- • Frequent phone calls.
- • Unsolicited phone calls.
- • Unscheduled visitors.
- • Unscheduled meetings.
- • Poor planning.
- • Poor delegation.
- • Over-commitment.
- • Sudden emergencies in the workplace.
- • The secretary got sick.
- • The assistant did not come to work.
|
- • Traveling delays.
- • Waiting for customers.
- • Canceled appointments.
- • One party is not available.
- • The contacted person does not have the authority to make decisions.
- • The contacted person does not need the product or service.
- • Unreliable car.
- • Wrong supporting documentation.
- • Wrong samples.
|
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
12. THE TEN COMMANDMENTS OF EFFECTIVE TIME MANAGEMENT |
 |
|
|
EFFECTIVE TIME MANAGEMENT
The Ten Commandments Of Effective Time Management outlined below are designed to provide a universal set of guidelines to business owners, managers, and sales people alike. |
THE TEN COMMANDMENTS OF EFFECTIVE TIME MANAGEMENT |
1. Organize Your Workplace.
Once you organize your workplace, you will be able to find documents and all other items which you may have been wasting time looking for from time to time.
2. Plan Your Schedule.
When your schedule is planned at least one week in advance, you may be surprised to discover how you suddenly find extra time to do things that you couldn't do before.
3. Delegate Work To Your Assistant.
Don't become your own bottle-neck. Use your common sense and delegate, delegate, and delegate. Then check and verify.
4. Do The Job Right The First Time Around.
Every time when you do something wrong - it will cost you triple time. The first time - when you did it wrong initially. The second time - when you took time to redo it, and the third time - by not using the second time for doing something else.
5. Don't Procrastinate.
Do today what you are supposed to do tomorrow whenever possible.
6. Shorten Your Phone Conversations.
If you don't watch your time in a chess game you may find yourself "out-of-time" and lose the game. Apply chess principles to your phone conversations and you will save a "ton" of time. You will be surprised at how easy it is.
7. Shorten Your Meetings.
Prepare a meeting agenda and avoid running the meeting in circles. You will save not only your own time but everybody's else too. Imagine how much extra work can be done in the saved time.
8. Reduce Your Unplanned Appointments.
The more you plan your time in the short-term, the more time you will save in the long-term. This works all the time.
9. Plan Your Travel Time.
It's always difficult to predict traffic jams on freeways, so plan your travel time in advance as much as you can to avoid wasting time on the road. Don't forget to use updated maps or, even better, install a navigation system in your car. This will save you time – “big time”.
10. Treasure Your Time.
You must remember that time is an irreplaceable commodity - once it's gone - it cannot be replaced. |
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
13. THE MAGIC TOOL FOR IMPROVED SALES PRODUCTIVITY |
 |
|
THE MAGIC TOOL FOR IMPROVED SALES PRODUCTIVITY
The Internet has become a magic tool for Improved Sales Productivity. Sales people should be prepared to take full advantage of numerous proven and cost-effective methods offered by various service providers online.
Three such examples are:
• Go To Meeting
• Join.me
• Webex
These services enable sales people to communicate with prospects and actual customers on many different levels. This may include providing detailed sales demonstrations of products and services, explaining their benefits and features, and providing any relevant information which may be requested by prospects and customers in real time. All this can be accomplished by sales people without leaving their office, thereby providing a powerful time-saving and cost-effective sales opportunity.
|
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
14. MAINTENANCE OF CUSTOMERS' RECORDS |
 |
|
IMPORTANCE OF MAINTAINING CUSTOMER RECORDS
Maintenance of Detailed Customer Records is another critical element of successful selling. The sales manager should guide each sales person in gathering and recording updated information on each customer in a Customer Record Sheet. This record includes the basic details about a specific customer such a company’s name, address, phone and e-mail address, contact names and phone numbers, and details regarding all transactions.
A typical customer record sheet is illustrated below. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
15. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
CUSTOMER RECORD SHEET |
 |
|
CUSTOMER RECORD SHEET |
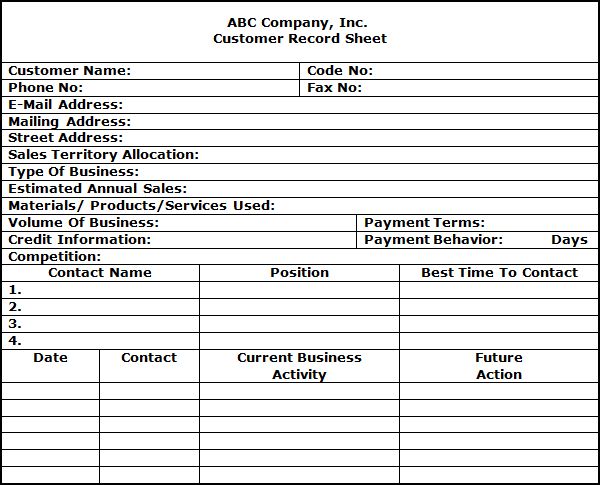 |
|
|
16. SALES CALL SCHEDULES |
 |
|
IMPORTANCE OF THE SALES CALLS SCHEDULES
Continuous updating of customer records helps sales people identify immediate customer requirements and develop appropriate Sales-Call Schedules. These schedules are designed to assist the sales person to maintain an effective time-management process.
Each sales-call schedule is usually prepared in advance on a weekly basis and it includes names of various individuals and organizations. A typical sales-call schedule is illustrated below. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
17. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
SALES CALLS SCHEDULE |
 |
|
SALES CALLS SCHEDULE |
Sales Person: |
Period: |
Time |
Monday |
Tuesday |
Wednesday |
Thursday |
Friday |
8:00 |
|
|
|
|
|
9:00 |
|
|
|
|
|
10:00 |
|
|
|
|
|
11:00 |
|
|
|
|
|
12:00 |
|
|
|
|
|
1:00 |
|
|
|
|
|
2:00 |
|
|
|
|
|
3:00 |
|
|
|
|
|
4:00 |
|
|
|
|
|
5:00 |
|
|
|
|
|
6:00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18. SALES ROUTES SELECTION |
 |
|
SELECT SALES ROUTES
Selection of Sales Routes is another important area where sales people often require guidance. Careful selection of sales routes is important for several reasons outlined below. |
REASONS FOR SELECTING SALES ROUTES |
1. |
To minimize the travel time and expenses. |
2. |
To increase the number of sales calls. |
3. |
To produce better sales results. |
|
Several rules are frequently used to select the most cost-effective sales routes. Some of these rules are outlined below. |
RULES FOR SELECTING THE MOST COST-EFFECTIVE SALES ROUTES |
1. |
Sales routes should be circular. |
2. |
Sales routes should never cross. |
3. |
The same sales route should not be used more than once during one day. |
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
19. MOTIVATE SALES PEOPLE IN MEETING THEIR OBJECTIVES |
 |
|
STEP 6: MOTIVATE SALES PEOPLE IN MEETING THEIR OBJECTIVES
Once a routine is established, the sales manager must ensure that sales people are constantly motivated to meet their individual objectives. The basic principles of Employee Motivation are discussed in detail in Tutorial 2. The basic guidelines of employee motivation include several Factors outlined below. |
EMPLOYEE MOTIVATION FACTORS |
1. |
Attractive remuneration. |
2. |
Employee benefits. |
3. |
Work security. |
4. |
Interpersonal functional relations. |
5. |
The opportunity to advance. |
6. |
Work challenge and satisfaction. |
7. |
Safe and comfortable working conditions. |
8. |
Fair and competent management. |
9. |
Correct guidance and reasonable orders. |
10. |
Credit for good performance. |
11. |
Sound social organizational structure. |
|
Additional employee motivation factors which are particularly useful in sales management are outlined below. |
SPECIAL MOTIVATORS FOR SALES PEOPLE |
1. |
Regular sales contests. |
2. |
Recognition awards or prizes for special achievement. |
3. |
Motivational and sales seminars. |
4. |
Group trips to exciting places. |
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
20. CONDUCT REGULAR SALES MEETINGS |
 |
|
STEP 7: CONDUCT REGULAR SALES MEETINGS
The final important element in the sales force management and motivation process is a Sales Meeting. The prime purpose of a sales meeting is to develop and maintain effective communication between the sales manager and each member of the sales team.
In order to ensure meaningful results, each sales meeting must be planned in advance. This entails preparation of a Sales Meeting Agenda which may include several topics outlined below. |
ELEMENTS OF A SALES MEETING AGENDA |
1. |
Sales force progress report regarding sales results. |
2. |
Sales force feedback regarding developments in the marketplace. |
3. |
Reports related to the competition activity in the marketplace. |
4. |
Sales training regarding existing products or services. |
5. |
New product or service introduction and training. |
6. |
Motivational talk or presentation. |
7. |
Announcement of a new compensation or incentive program. |
8. |
Recognition of sales performance and awards for sales people. |
|
| |
SALES REPORTING PROCEDURE |
|
Sales Meetings must be conducted on a regular weekly or bi-weekly basis to ensure continuous communication within the sales department. Sales meetings also provide an opportunity for sales people to report their Individual Progress and introduce relevant details concerning customers.
Business owners and sales managers should also consider the use of the following online communication tools for conducting sales meetings with sales people located in various sales offices:
• Go To Meeting
• Join.me
• Webex
Each of these options will provide time and cost-effective solutions for the company and all participants when sales people are located far away from the main office. Moreover, these options will enable the sales people to report their sales results to the main sales office without excessive driving, thereby improving the overall sales performance efficiency.
The reporting procedure involves completion of a Sales Progress Report, and enables the sales manager to monitor current results and evaluate business potential. A typical sales progress report is presented below.
All Actual Results achieved by each sales person and recorded in the sales progress report must be summarized on a monthly and year-to-date basis. Subsequently, these results need to be compared with the corresponding sales quotas to determine respective variances. The aforementioned procedure provides the foundation for Sales Performance Evaluation And Control, discussed in detail in Tutorial 5. |
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
21. SMALL BUSINESS EXAMPLE
SALES PROGRESS REPORT |
 |
|
SALES PROGRESS REPORT |
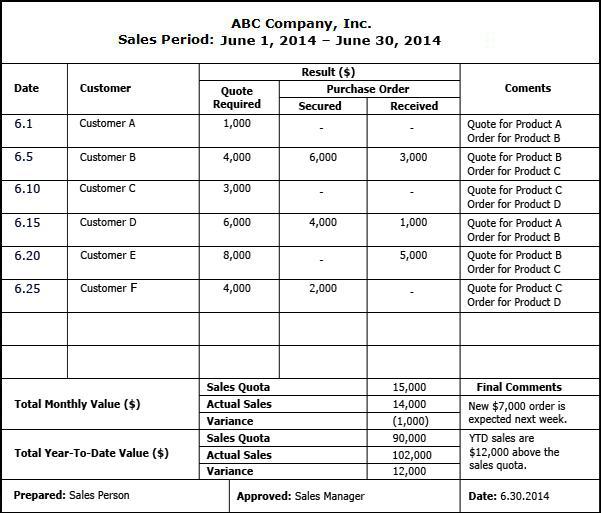 |
|
|
22. CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE PROGRAMS |
 |
|
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE PROGRAMS
There are several Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software programs specifically developed for sales managers and sales people in small and medium-sized companies. These programs are designed to assist sales people to manage their relationships with customers in a more time- and cost-effective manner to ensure higher profitability of their organization.
Some providers offer CRM software programs based on a “one-size fits all” solutions and for this reason, such programs may not be practical for all users. Other providers offer CRM programs which offer custom-designed features for their users. These programs are definitely more popular in the marketplace.
Some of the most popular CRM software programs used by millions users are presented below:
• Act CRM
• NetSuite CRM
• Salesforce CRM
• OnContact CRM
• Maximizer CRM
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
23. FOR SERIOUS BUSINESS OWNERS ONLY |
 |
|
ARE YOU SERIOUS ABOUT YOUR BUSINESS TODAY? |

Reprinted with permission. |
|
24. THE LATEST INFORMATION ONLINE |
 |
|
| |
LESSON FOR TODAY:
Good Motivation Is The Art Of Getting Average
Sales People To Achieve Above-Average Results!
|
Click Here And Find Out How You Can Benefit From Lean Business Club. |
| |
|








