HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT
CHECK POINT 39: EMPLOYEE SAFETY AND HEALTH
This Check Point Is Available By Subscription Only,
But You Can Still Check Out The Menu Below. |
|
|
| |
|
DO I NEED TO KNOW THIS CHECK POINT?
|
| |
HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT
CHECK POINT 39: EMPLOYEE SAFETY AND HEALTH
Please Select Any Topic In Check Point 39 Below And Click. |
|
|
| |
|
DO I NEED TO KNOW THIS CHECK POINT?
|
| |
WELCOME TO CHECK POINT 39 |
|
| |
HOW CAN YOU BENEFIT FROM CHECK POINT 39? |
| |
| The main purpose of this check point is to provide you and your management team with detailed information about Employee Safety And Health and how to apply this information to maximize your company's performance. |
| |
| In this check point you will learn: |
| |
• About work accident related statistics
• About the reasons for effective safety and health procedures.
• About action required for employee safety and health.
• About the basic OSHA standards and how to apply them in a company.
• About safety programs in small and medium-sized medium companies.
• About a company's specific safety requirements.
• About safety education and training of employees.
• About technical and human factors leading to accidents.
• About reporting of work-related accidents.
• About record-keeping and accident analysis systems... and much more. |
| |
LEAN MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES FOR CHECK POINT 39 |
| |
| You and your management team should become familiar with the basic Lean Management principles, guidelines, and tools provided in this program and apply them appropriately to the content of this check point. |
| |
| You and your team should adhere to basic lean management guidelines on a continuous basis: |
| |
| • |
Treat your customers as the most important part of your business. |
| • |
Provide your customers with the best possible value of products and services. |
| • |
Meet your customers' requirements with a positive energy on a timely basis. |
| • |
Provide your customers with consistent and reliable after-sales service. |
| • |
Treat your customers, employees, suppliers, and business associates with genuine respect. |
| • |
Identify your company's operational weaknesses, non-value-added activities, and waste. |
| •. |
Implement the process of continuous improvements on organization-wide basis. |
| • |
Eliminate or minimize your company's non-value-added activities and waste. |
| • |
Streamline your company's operational processes and maximize overall flow efficiency. |
| • |
Reduce your company's operational costs in all areas of business activities. |
| • |
Maximize the quality at the source of all operational processes and activities. |
| • |
Ensure regular evaluation of your employees' performance and required level of knowledge.
|
| • |
Implement fair compensation of your employees based on their overall performance.
|
| • |
Motivate your partners and employees to adhere to high ethical standards of behavior. |
| • |
Maximize safety for your customers, employees, suppliers, and business associates. |
| • |
Provide opportunities for a continuous professional growth of partners and employees. |
| • |
Pay attention to "how" positive results are achieved and constantly try to improve them. |
| • |
Cultivate long-term relationships with your customers, suppliers, employees, and business associates. |
|
|
|
1. STATISTICS ABOUT WORK-RELATED ACCIDENTS |
 |
|
STATISTICS ABOUT WORK-RELATED ACCIDENTS |
Business owners and managers must be fully familiar with a broad range of safety and health requirements to ensure adequate working conditions and the safety and health of all employees within the organization.
The United States Public Health Service reports that during one year, there were almost 8.5 million injuries as a result of accidents at work. The National Safety Council (NSC) reports over 14,000 deaths over the same period.
Many experts, in fact, believe that the actual numbers are much higher. Furthermore, these figures neither reflect the pain and suffering of employees and their families, nor include the tremendous costs of medical treatment, lost working hours, and litigation expenses. |
You can obtain additional statistics about the work-related accidents online from: |
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
2. REASONS FOR EFFECTIVE SAFETY AND HEALTH PROCEDURES |
 |
|
DO YOU HAVE SAFETY AND HEALTH PROCEDURES WITHIN YOUR ORGANIZATION? |
It is essential that you and your management team develop and implement effective Safety And Health Procedures within your organization. According to a safety expert Willie Hammer, there are several reasons for establishing effective safety and health procedures within any company as illustrated below. |
THREE MAIN REASONS FOR SAFETY AND HEALTH PROCEDURES |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
Moral Reasons |
|
Legal Reasons |
|
Economic Reasons |
The objective here is to secure the welfare of employees and their families. |
|
The objective here is to meet appropriate legislation. |
|
The objective here is to reduce injury compensation costs, medical expenses, and production losses. |
|
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
3. ACTIONS REQUIRED FOR EMPLOYEE SAFETY AND HEALTH |
 |
|
DO YOU PLAN YOUR SAFETY PROCEDURES IN ADVANCE? |
The development of effective Safety And Health Procedures necessitates that you and your management team plan certain actions in advance. Some of these actions are outlined below. |
ACTIONS REQUIRED FOR EMPLOYEE SAFETY AND HEALTH |
1. |
Select a person among the managerial staff who will be responsible for the safety and health of employees. |
2. |
Ensure safety within the organization and particularly operational safety within the operations department. |
3. |
Provide sufficient education in safe operational performance to employees. |
4. |
Keep sufficient records related to safety maintenance procedures. |
5. |
Formulate and enforce all instructions related to employee safety and health. |
|
| |
|
You should also develop specific procedures related to Job Safety Analysis (JSA) and ensure that every employee is familiar with relevant safety procedures and guidelines for handling various types of equipment, machinery and hazardous materials. |
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
4. THE BASIC OSHA STANDARDS |
 |
|
THE BASIC OSHA STANDARDS |
The safety and health procedures should be developed in accordance with standards set by the Occupational Safety And Health Administration (OSHA).
The Basic OSHA Standards state that every employer:
"...shall furnish, to each of his employees, employment and a place of employment which are free from recognized hazards that are causing or are likely to cause death or serious physical harm". (46)
Under the provisions of The Occupational Safety And Health Act Of 1979, OSHA's standards are enforced nation-wide through the offices of the U.S. Department Of Labor. These standards are very comprehensive and apply to all employers except self-employed persons, self-employed farmers and members of their families, and other work places that are regulated by similar standards.
Managers should be aware that several states have created their own OSHA Standards which are sometimes more strict than those created by the Federal Occupational Safety and Health Administration.
Some states, for example, mandate quarterly safety training for all employees. In most states, companies can ask for a voluntary OSHA inspection to assure that they are in compliance. A voluntary OSHA inspection, in fact, may be beneficial to the company for a number of reasons, as outlined below. |
BENEFITS OF A VOLUNTARY OSHA INSPECTION |
1. |
It simply is the right thing to do. |
2. |
It may help identify areas where the safety of employees is not adequate. |
3. |
It may avoid possible accidents and injuries of employees. |
4. |
It may improve the morale of employees. |
5. |
It may help avoiding unnecessary lawsuits. |
6. |
It may be economically wise. |
7. |
It may improve the overall productivity and, ultimately, the "bottom line". |
|
| |
ADDITIONAL OSHA GUIDELINES |
If OSHA finds that a particular company does not meet its standard requirements, that company will be given a time frame for correcting the problem or problems without penalty.
Managers should be also aware that according to OSHA's Guidelines, a company can't retaliate against an employee who may decide to file a complaint against the company with an OSHA office. |
Please check with your Local OSHA Representative regarding various safety requirements in your state by phone: (800) 321-OSHA or (800) 321-6742.
You can also obtain additional information about OSHA – U.S. Department Of Labor online. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
5. APPLICATION OF THE BASIC OSHA STANDARDS |
 |
|
THE BASIC OSHA STANDARDS |
The Basic OSHA Standards for general industry, for example, are set for a broad range of items and activities. (47) |
APPLICATION OF THE BASIC OSHA STANDARDS |
1. |
Walking-working surfaces. |
2. |
Powered platforms, lifts, and vehicle-mounted work platforms. |
3. |
Occupational health and environmental control (ventilation, sanitation, etc.). |
4. |
Hazardous materials. |
5. |
Protective equipment for employees. |
6. |
Medical and first aid. |
7. |
Compressed gas and compressed air equipment. |
8. |
Materials handling and storage. |
9. |
Machinery and machinery guarding. |
10. |
Hand and portable powered tools and other hand-held equipment. |
11. |
Welding, cutting, and braising. |
12. |
Special industries (textile, chemical, paint, food, etc.). |
13. |
Electrical installations and equipment. |
14. |
Toxic and hazardous substances. |
15. |
Fire protection. |
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
6. SAFETY PROGRAMS IN SMALL AND MEDIUM-SIZED COMPANIES |
 |
|
SAFETY PROGRAMS IN SMALL AND MEDIUM-SIZED COMPANIES |
Safety Programs in small and medium-sized companies are usually developed by managerial employees who are directly involved in the operational activities of the organization.
As safety expert Willie Hammer suggests: "A prime requirement for any successful accident prevention program is to leave no doubt in the mind of any employee that his or her managers are concerned about accident prevention."
The most effective means by which this can be done is that the manager at the highest level possible issues a directive indicating the Accident Prevention Policies and then to ensure that the lower-level managers and supervisors carry them out. If the company's management does not take the safety issues seriously, other employees will not either. |
You can obtain additional information about various Safety Programs provided by OSHA – U.S. Department Of Labor online. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
7. COMPANY'S SPECIFIC SAFETY REQUIREMENTS |
 |
|
SAFETY REQUIREMENTS |
It is essential that you and your management team examine your company's Specific Safety Requirements and ensure, whenever necessary, that the following objectives are met, as outlined below. |
COMPANY'S SPECIFIC SAFETY REQUIREMENTS AND OBJECTIVES |
1. |
The operational facility is well lit, properly ventilated, and kept in generally clean condition. |
2. |
Mechanical equipment is adequately safeguarded. |
3. |
Electrical installations are sufficiently insulated and grounded. |
4. |
Production and operations processes involving various mechanical movements, such as press brakes or guillotines, have a dual activation system. |
5. |
Tanks containing poisonous liquids or chemical solutions are isolated and surrounded by special safety guards, false floor installations, and fume protection and extraction systems. |
6. |
Tanks and boilers operating under high temperature and pressure have sufficient thermal insulation and proper structural reinforcement. |
7. |
Dust-producing plants incorporate efficient air pollution control systems. |
8. |
Operators are issued special safety overalls, goggles, boots, gloves, and other protective items. |
|
| |
ADDITIONAL SAFETY REQUIREMENTS |
Management should also ensure that Employees do not attempt to modify safety precautions that usually present some form of a mechanical delay or an additional operation. It is also essential to enforce that employees wear all personal protective clothing and use the right equipment during working hours. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
8. SAFETY EDUCATION AND TRAINING OF EMPLOYEES |
 |
|
SAFETY EDUCATION AND TRAINING OF EMPLOYEES |
Education And Training of employees represents another important avenue of ensuring conditions for safe performance within the company. The Safety Education should start during the process of the employees' orientation to their jobs and should continue throughout the job performance by means of several safety education methods outlined below. |
SAFETY EDUCATION METHODS IN THE WORKPLACE |
1. |
Safety instructions during the orientation and training sessions. |
2. |
Safety precautions during the on-the-job training program. |
3. |
Safety procedures established by management. |
4. |
Operational meetings regarding safety requirements. |
5. |
Explanatory posters and charts describing the safety procedures. |
|
You can obtain additional information about Safety Education And Training Of Employees provided by OSHA – U.S. Department Of Labor online. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
9. FACTORS LEADING TO ACCIDENTS |
 |
|
ACCIDENTS |
Safety experts believe that there are two distinctive factors which may lead to Accidents in industry as illustrated below. |
TWO TYPES OF FACTORS WHICH MAY LEAD TO ACCIDENTS |
 |
|
 |
Technical
Factors |
|
Human
Factors |
|
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
10. TECHNICAL FACTORS |
 |
|
TECHNICAL FACTORS |
Technical Factors represent a cause related to plant, equipment, tools, materials, and overall working environment deficiencies. Some of the typical technical factors, which may cause problems in the workplace, are outlined below. (48) |
TECHNICAL FACTORS WHICH MAY CAUSE PROBLEMS IN THE WORKPLACE |
1. |
Improperly guarded equipment. |
2. |
Defective equipment. |
3. |
Hazardous arrangement of procedures or materials in, on, or around, machines or equipment. |
4. |
Unsafe storage, congestion, or overloading of materials and equipment. |
5. |
Improper illumination, glare, or insufficient light. |
6. |
Improper ventilation, insufficient air change, impure air source. |
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
11. HUMAN FACTORS |
 |
|
HUMAN FACTORS |
Human Factors represent a cause related to unsafe behavior of employees in the workplace. Some of the typical human factors, which may cause problems in the workplace, are outlined below. (49) |
HUMAN FACTORS WHICH MAY CAUSE PROBLEMS IN THE WORKPLACE |
1. |
Failing to secure equipment. |
2. |
Failing to use safe attire or personal protective equipment. |
3. |
Throwing materials and tools. |
4. |
Operating or working at unsafe speeds, either too fast or too slow. |
5. |
Making safety devices inoperative by removing, adjusting, or disconnecting them. |
6. |
Using unsafe equipment or using equipment unsafely. |
7. |
Using unsafe procedures in loading, placing, or mixing materials. |
8. |
Taking unsafe positions under suspended loads. |
9. |
Lifting equipment, materials, or products improperly. |
10. |
Distracting, teasing, abusing, startling, quarreling, horse playing. |
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
12. OCCUPATIONAL INJURY AND ILLNESS RECORD |
 |
|
OCCUPATIONAL INJURY AND ILLNESS RECORD |
Approximately 80% of all accidents in industry are caused by the Human Factor. Management should realize, therefore, that a well-designed Safety Program, combined with steady Education and Occupational Training of employees, may substantially contribute to the company's accident-free performance.
According to OSHA Requirements, every employer with 11 employees or more must maintain a set of occupational injury and illness records. Small businesses with fewer than 11 employees are generally exempt from the record-keeping procedure. Basic details of this procedure are presented below. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
13. REPORTING OF WORK-RELATED ACCIDENTS |
 |
|
OSHA REPORTING PROCEDURES |
Management should adhere to specific Reporting Procedures developed by OSHA in case of work-related accidents as illustrated below. |
REPORTING OF WORK-RELATED ACCIDENTS UNDER
THE OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH ACT (OSHA) |
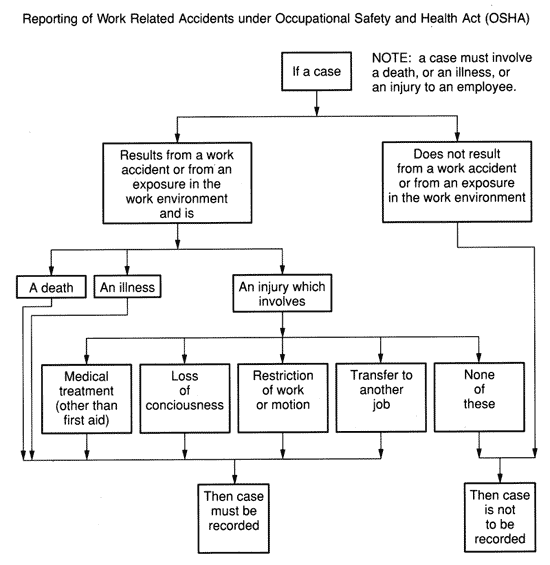 |
|
© What Every Employer Needs to Know About OSHA Recordkeeping, Washington DC.: US Department of Labor |
You can obtain updated information about the Accident Reporting Procedures prescribed by OSHA – U.S. Department Of Labor online. |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
14. RECORD-KEEPING AND ACCIDENT ANALYSIS SYSTEM |
 |
|
RECORD-KEEPING AND ACCIDENT ANALYSIS SYSTEM |
Management should ensure a complete and updated record-keeping system related to the company's accidents and should conduct a proper accident analysis. A typical Record-Keeping And Accident Analysis System should include a broad range of related issues outlined below. |
ELEMENTS OF A RECORD-KEEPING AND ACCIDENT ANALYSIS SYSTEM |
1. |
Details of an employee's injury and reasons for the accident. |
2. |
Costs of replacing the injured employee and cost of personnel investigating the accident. |
3. |
Cost of damage to the production facility, equipment, and materials caused by the accident. |
4. |
Cost of compensation to the injured employee and his or her family as a result of the accident. |
5. |
Miscellaneous costs related to the accident. |
|
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
15. MANAGEMENT ACTION FOR AN ACCIDENT-FREE ENVIRONMENT |
 |
|
IMPORTANCE OF WORKING CONDITIONS |
Health of the company's employees represents another factor in the process of maintaining an Accident-Free Working Environment. Management, therefore, should provide working conditions that will prevent any adverse effect on the physical and mental state of the employees.
In order to create an accident-free environment, management should undertake a number of steps outlined below. |
MANAGEMENT ACTION FOR AN ACCIDENT-FREE ENVIRONMENT |
1. |
Analyze all aspects of the company's operational activities and identify the stage that represents potential health hazards. |
2. |
Prepare a standard procedure related to the actual accident-handling process. |
3. |
Formulate a health and medical insurance policy. |
4. |
Sponsor medical examinations for all employees exposed to health hazards. |
5. |
Provide systematic attention to industrial hygiene and sanitation. |
6. |
Encourage regular medical examinations for all employees. |
|
| |
ROLE OF AN INDUSTRIAL HYGIENIST |
Management is also advised to call upon the services of an Industrial Hygienist to establish an adequate level of health and a hazard-free working environment within the organization. The industrial hygienist is trained to identify operational hazards, to assess the probability of possible accidents, and to design health programs that will ensure desirable working conditions. |
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
16. OCCUPATIONAL STRESS FACTORS |
 |
|
OCCUPATIONAL STRESS FACTORS |
Managers should also be prepared to deal with Health Problems such as drug addiction, alcoholism, or emotional illness. These problems may sometimes occur as a result of Occupational Stress, or Job Stress. Occupational stress places an undesirable burden on the mental and physical state of the employee and may be detrimental to his or her health.
Regardless of its source, occupational stress affects the well-being of employees and has an adverse effect on Job Performance. This, in turn, causes increased frustration, absenteeism and turnover rate of employees, and subsequent deterioration of the company's performance. In order to prevent such a condition, it is essential to identify and assess the following factors illustrated below. |
TWO MAIN FACTORS RELATED TO OCCUPATIONAL STRESS |
 |
|
 |
Environmental Factors |
|
Personal Factors |
These include the degree of safety and comfort in the workplace and workload, the nature of duties, types of customers, and the sense of job security. |
|
These include the employee's personality, ability to handle stress, attitude toward work and employees, stress in personal life, and state of physical and mental health. |
|
|
| |
WHAT IS AN EMPLOYEE ASSISTANCE PR0GRAM (EAP)? |
A new program has become popular in recent years with many employers. This program is called Employee Assistance Program (EAP) and is designed to address a broad range of issues related to occupational stress among employees.
Note:
Additional information regarding the Employee Assistance Program (EAP) may be obtained from the Member Benefits Department at Lean Business Club by e-mail: Info@LeanBusinessClub.com. |
| |
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ONLINE |
|
|
|
17. FOR SERIOUS BUSINESS OWNERS ONLY |
 |
|
ARE YOU SERIOUS ABOUT YOUR BUSINESS TODAY? |

Reprinted with permission. |
|
18. THE LATEST INFORMATION ONLINE |
 |
|
| |
LESSON FOR TODAY:
Safety Does Not Happen By Accident!
|
Go To The Next Open Check Point In This Promotion Program Online. |
| |
|





